Guide Introduction
Online learning has become a strong contender as one of the most exciting, fastest-growing industries of the past ten years (2010 – 2020).
Disruptors in the eLearning industry are giving the traditional multi-billion dollar education industry a serious run for their money by attracting mass interest with their alternative, online learning options.
However, as the online education space gets more and more competitive, acquiring a student through the means of digital advertising becomes more challenging and therefore less profitable.
We developed this comprehensive guide to drive profitable enrollments at scale with Google Ads. Our strategies are based on the biggest challenges faced by education marketers, which we discovered by surveying them on their struggles with acquiring new enrollments. This guide is designed to provide solutions to this extremely daunting task.
Our strategies are also built on 5 years of testing and over $100m in budgets. They will work today and continue to work for the next 4-5 years at the very least. Certain sections of this guide are highly technical and may fall outside of your job description. But that just goes to show how complex an effective ad strategy must be in 2020.
The Latest Trends in Student Digital Engagement
In order to create a comprehensive omni-channel Google Ads strategy for EDU, we first analyzed how prospective students are researching education companies online.
With this data, we can determine:
- How students are conducting their research (which devices, channels, etc.).
- What students are researching (which questions are they asking, which keywords are they searching, which YouTube videos are they watching, which blog articles are they reading, etc.)
- How students are making the decision to choose one opportunity over another.
Answering these questions gives us a thorough understanding of the latest digital engagement trends for prospective students. Throughout this guide, we will reference the following data points:
- On average, prospective students engage with more than 1,000 digital touchpoints while researching programs in a 6-week period before filling out a lead form.
- In Q4 of 2019, certification program-related queries grew more than 15% YoY.
- In Q4 2019, the average CPC with an “online” modifier was $22, which is 5X greater than the average CPC for terms without the “online” modifier.
- Prospective students are 60% more likely to move down the funnel after watching online videos related to their desired program.
- 83% of prospective students watch YouTube an average 3+ times a day.
- Post-lead submission students engage in 1.5x as many digital activities as pre-lead submission students.
- 56% of prospective students begin their research on Google.
- Students who enroll are 2X more likely to fill out 3+ lead forms, compared to students who do not enroll.
Google Ads Audience Overview For Search, YouTube & Display
With prospective students moving through different stages of their research funnel and using multiple platforms in the process, understanding the type of audience categories that Google Ads has to offer will provide the clarity you need to make smarter strategic decisions.
This also allows you to better anticipate your prospects’ interests and preferences while delivering the right marketing message at exactly the right time, whether you’re using Search, Display, or YouTube.
YouTube / Display
For YouTube / Display, we have the ability to strategically connect with prospective students at every stage of the journey.

Below are all the available audiences that advertisers can utilize on both channels:
Detailed Demographics – Target prospective students through basic information like parenting stages, home ownership status, marital status & education.
Affinity – Target prospective students through interests and lifestyle choices. Google distinguishes users who are truly passionate about a topic from those who have expressed slight interest at best.
Custom Affinity – Target prospective students based on their interactions across Google Search, Maps, YouTube and Android app download data.
Life Events – Target prospective students as they approach important milestones and are more likely to make major purchases.
In-Market – Target prospective students who are actively researching and intend to enroll in any education company.
Custom Intent – Target prospective students who are actively researching your programs on Google.com, so you can then advertise to them on YouTube.
Customer Match – Cross-sell or upsell students who are currently enrolled in your program.
Remarketing – Reconnect with prospective students who have previously engaged with your education company to get them to enroll.
Similar Audience – Broaden your targeting by reaching prospective students who share the characteristics associated with any of the previous audience types.
Search Audience Options
Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSA): This audience allows you to modify bids on search traffic from previous website visitors. You can also segment bidding even further by separating previous website visitors based on levels of site engagement (viewed specific pages, interacted with lead forms, spent at least a certain amount of time on the site, etc.).
Customer Match: These are audiences created by pulling student email addresses from CRM systems.
Similar Audiences: You create a list of audiences (application submissions, enrollments, etc.) and then Google advertises to people who are similar to these audiences.

Using Audiences With Search
How does audience targeting affect your search strategy in the first place? There are three main benefits to layering on audiences to your search campaigns:
Variable bidding – Bid up or down based on expected or known audience value or priority
Query expansion – Advertise on a broader set of queries based on additional audience relevance signals
Creative Customization – Maximize ad relevance by customizing language or offers by audience types
The Importance of Omni-Channel Marketing
Earlier, we established that prospective students engage with more than 1,000 digital touchpoint before filling out their first lead form.
What is a digital touchpoint?
A digital touchpoint is when a prospective student engages with a piece of digital content that plays a role in their next decision in their educational paths.
Video content, blog articles, social media posts, research reports, testimonials, eBooks, and course details can all be the setting of digital touchpoints. As digital marketers, we can showcase our brand as THE top choice, regardless of the channel and where the prospective student is in the funnel.
How many digital touchpoints do you think you are currently serving on?
How many more enrollments do you think you could acquire if you were able to be a part of most of those touchpoints?
Developing an Omni-Channel approach allows you to be at the right place at the right time.
Below, we provide strategies and explain the importance of an omni-channel digital marketing approach.
Cold Traffic Introduction (Top of Funnel (Awareness)
As prospective students browse the web, data is being sent back to Google, where it gets filtered into different audiences. This data allows education marketers to target prospective students at specific points in their marketing funnel. The first stage of the funnel is known as “Awareness.”

This is merely an introduction to your education company and the prospective student’s desired program. The two audiences that fit under the Awareness stage are Affinity and Custom Affinity.
These audiences can represent prospective students who are considering a career change, prospective students looking to advance their current career, recent high school graduates, or college graduates looking for post-secondary online learning options.
For example – John Don has an interest of a new career in data science. He wants to learn the required skills but doesn’t know where to start. He starts researching with an intent to learn more about data science. In this case, we have the opportunity to lead John into a video content sequence that provides value-based content, instead of trying to enroll him right away.
83% of prospective students watch YouTube 3X a day. Engaging prospective students during the Awareness phase makes them 60% more likely to fill out a lead form.
ACTION: Create Affinity audiences / Custom Affinity audiences based on the programs you are trying to promote with YouTube / Display advertising.
If your goal is to target John Don who is looking for a new career in data science, your affinity audience could be technophiles in the 24-35 range.
You can also layer on some Custom Affinities by including prospects who have been reading about data science or have used apps related to those categories.
Keep in mind, a custom affinity for a website will be based on site content, not site visitors.
You can find the full list of affinity audiences here.
More details on custom affinity here.
ACTION PART 2: Launch high funnel YouTube campaigns that target prospective students who have just begun the research phase. Make sure to set a high frequency per user for these audiences. This way, even if a prospective student doesn’t engage with your content, they will have your company in their head when they are ready to make a decision.
Also, your creative should be catchy and brand-focused. This will make it easier for prospective students to remember your company and programs.
As for targeting, you can build Affinity audiences for users who are searching high funnel research terms, such as “what is data science,” “data science skills,” or even “data science growth.”
(For more ideas on campaign structure and strategies please see Structure and Strategy section)
Warm Traffic Presence (Mid-Funnel) (Consideration)
Once the prospective student passes the Awareness phase, several scenarios may transpire, all of which are below:

SEM
56% of prospective students begin researching names of programs or education companies on Google after passing the Awareness phase.
If your Awareness strategy was effective, you will see an increase in prospective students searching for your company (which is what we want) rather than a generic term like “data science online course.”
It’s imperative to be active on Google search (Branded & Non-Branded) so we can engage prospective students in the mid-funnel stage and capture the lead.
ACTION: Launch Branded and Non-Branded campaigns with the goal of driving high quality leads through your enrollment process.
Also, layer search audiences to improve visibility for prospective students. This gives you the opportunity to add additional bidding modifiers.
(For ideas on campaign structure & strategies please see below).
YouTube
83% of prospective students watch YouTube an average 3+ times a day. The sheer popularity of YouTube with prospective students is all the reason we need to include this channel in our strategy across all funnel steps.
Prospective students are 60% more likely to move up in their journey (or down the funnel) after watching videos related to their desired program. This makes YouTube particularly important for In-Market Audiences, who are actively researching and on the verge of making an enrollment decision.
ACTION: Create In-Market YouTube strategies with creative that resonates with prospective students who intend to follow through on their research and submit a lead form.
You can find the full list of In-Market audiences here.
Very Warm Traffic (Bottom of Funnel) Action)
Bottom funnel prospective students fall into one of two categories: those who have submitted a lead form and those who have not.

NOT SUBMITTED A LEAD FORM
Remarketing Audience – Reconnect with prospective students who have previously engaged with your company and turn them into students.
These prospective students have shown interest, but are close to taking action on requesting more information. Therefore, we must continue to provide valuable content to drive them back to our website.
ACTION: Create remarketing audiences broken out by segments of days and launch action-driven video content. Possible ideas for content can include USPs, success stories, promotion, etc.
Custom Intent – Reach prospective students who are actively searching for your company on Google.com in order to drive action on YouTube.
Custom Intent is one of the most powerful strategies you can utilize on YouTube. It allows you to create an audience based on specific keywords that prospective students searched on Google but did NOT click your ad. This gives us the opportunity to advertise to prospective students who are very likely to make an enrollment decision.
ACTION: Put together a list of 50 keywords that each have at least 1M impressions per month in order to launch a custom intent YouTube campaign. The creative should be focused on bottom of the funnel, action-driven content.
SUBMITTED A LEAD FORM
Lead form submission (re-engagement)
Our work on the digital marketing front is not done once a prospective student fills out a lead form. The next step is to add these students to the “Completed Lead Form” custom audience.
We want to continue advertising to this audience to show them what it looks like to be a student at your education company.
Prospective students fill out an average of 6+ lead forms before making an enrollment decision. Re-engagement strategies allow us to turn more leads into enrollments instead of just adding as many leads as possible to the top of the funnel.
ACTION: Create a “completed lead form” custom audience. Then, create a specific ad group for this initiative and launch action-driven content to reinforce their decision for requesting more information. Content ideas can include testimonials, success stories, etc.
Similar Audiences
Utilizing similar audiences allows the Google algorithm to look for prospective students that fit closely with your current student base or other prospects who have already filled out a lead form, submitted an application, or enrolled. These targets are extremely valuable because of their high interest in your program.
Campaign Structure & Strategies For SEM, YouTube & Display
Campaign structure within Google Ads is notoriously undervalued. Developing the correct campaign structure will create a healthy foundation for your campaigns to prosper over a 2-4 year period.
Without the right structure, your campaigns will deliver inconsistent numbers of leads and leads of inconsistent quality; resulting in frustration, confusion and ultimately a drop in enrollments.
It is important to note that there isn’t a universal structure that works for every company in every scenario. But, by aligning your goals or programs to your structure, you can develop a strategy that works best for your company.
We’ll start with campaign/ad group structure for SEM.
SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
Below, we have outlined a few different structure strategies depending on the type of data that is available and the number of program offerings.
Structure Example #1
Alpha – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Exact
Alpha – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – BMM
Alpha – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Phrase
Alpha – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Broad
Beta – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Exact
Beta – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – BMM
Beta – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Phrase
Beta – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Broad
Alpha – Only queries that have turned into a lead / application / enrollment (depending on which data is integrated into your Google Ads account).
Beta – If you have applications or enrollments data in your Google Ads platform, Beta queries are those that drive leads but not applications / enrollments for the purpose of testing. If you only have leads in your Google Ads platform, then Beta would be queries that are relevant but yet to generate a lead.
Structure Example #2
Local – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Exact
Local – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – BMM
Local – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Phrase
Local – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Broad
National – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Exact
National – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – BMM
National – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Phrase
National – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Broad
This structure is primarily geared towards companies that have both online and on-campus programs with the focus of enrolling students from within a 100-200 mile radius while also driving online enrollments from outside the local region. The separation of “Local” and “National” helps prioritize budgets broken out by these two segments.
Structure Example #3
This pertains to companies that offer programs in one primary field with overlapping subjects and keyword themes, i.e. medical online education.
Category 1 – Non-Branded – Exact
Category 2 – Non-Branded – Exact
Category 3 – Non-Branded – Exact
(campaigns get duplicated to BMM, Phrase and Broad)
Example Categories: General, Competitors, Specific Themes
Segmentation Explanations

The most important segmentation element today is breaking out your campaigns by match types. A few reasons why:
Match type data varies dramatically when it comes to performance and quality of leads, so it’s crucial to keep them separated at a campaign level. In the data example below, you’ll see that Exact has the most leads, cheapest CPL, and highest conversion rate (and highest lead quality because it’s Exact).
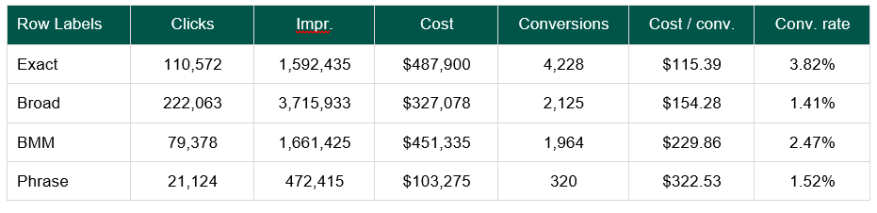
Broad has the second highest number of leads, but the lowest conversion rate. This means the quality of the leads is not as high when compared to Exact, BMM and Phrase. BMM / Phrase are more on the expensive side, but are also considered good quality because the words within the keyword exist in the query. The goal is to drive as many Exact leads as possible while using the other three match types to find new ways that people are searching for your program.
If you have a high number of poor quality leads, there is a high chance that the majority (80%+) of your budget is being spent on Broad match. Broad match can be highly effective if you have the proper campaign / negative keyword strategy in place (reference negative keyword section).
If you allow Broad match to be your primary match type, then your performance is going to vary tremendously on a daily basis and you will receive a significant amount of poor quality leads.
When your campaigns are broken out by match types, you gain the ability to do something called “Bid Tiering By Match Type.” This allows you to tier your bidding from highest to lowest (Exact to Broad).
The purpose of this bidding strategy is to force as much traffic to the Exact, Phrase and BMM match type; leaving Broad match as a completely exploratory match type that fishes for new search queries. Below is an example of how to effectively tier bidding for each match type.

HOT TIP – Be careful optimizing your Broad match campaigns. These campaigns have great potential for success, but you must make sure to not overpay for clicks by aggressively increasing your broad match CPCs.
Breaking out campaigns by match types also enables a strategy called “Cross-Match Negative Keywords.” This allows you to take all of your Exact match keywords and add them as a negative to the respective BMM, Phrase and Broad campaigns. The goal is to ensure that your Exact match keywords get all the Exact match traffic while forcing the BMM, Phrase & Broad campaigns to become the fishing match types; driving new traffic and growing the account.

Additionally, you should have a few different negative keyword lists.
Master Negatives – The bread and butter of negative keywords. Master Negatives eliminate irrelevant queries from showing up in an account. This must be done on a regular basis in order to keep the account clean, as new irrelevant search queries will never stop showing up. Google has previously confirmed that 25% of all daily search queries are being seen for the first time. If you’re using broad match, there will always be negatives to add to an account.
Weekly is the recommended frequency, but bi-weekly or monthly is acceptable once most high-frequency irrelevant queries have been added to your negative keyword list.
There should also be a break out between Exact match negatives from your Phrase match for easier damage control. When adding Phrase match negatives, be careful of what you add, as you could unknowingly end up excluding a lot of traffic.
Bad Quality Leads – These are queries that are driving leads, but are not driving applications or enrollments. We want to block all of these queries from all Phrase, BMM and Phrase match campaigns to ensure we are continuously striving to improve quality.
Poor lead quality is a controversial topic in the education space. It’s prevented many education marketers from reaching their goals and caused many admissions teams to waste precious time and money on unqualified leads, which ultimately decreases the time spent on higher quality leads.

Another reason you might be experiencing a high number of poor quality leads is incorrect keyword selection. In order to determine which keywords make sense for your company, someone who is knowledgeable about your programs needs to review them. This also ensures that whatever keyword is being selected has the intent (or nearly has the intent) of following through to register for the program.
If a Broad keyword is driving only irrelevant queries, it should be paused and analyzed for quality. If it is driving both relevant and irrelevant queries, the negative strategy outlined above will help improve the keyword’s performance over time.
If you have access to lead quality data on the query level, you can look for trends and add an additional level of negatives. For example, a private education company with a higher tuition will likely see worse performance from “cheap college degree” or “low cost design program” searches, even if both searches are driving leads.
Final tips on negatives
- Don’t apply negative lists to exact match campaigns
- Break out Exact VS Phrase match master negatives for easier management and damage control
- When doing cross match negatives, do not include keywords that are too long and can therefore be considered “low search volume” by Google. 40+ characters is a good guideline.
- Cross match negatives are only updated at the launch of the campaigns and when new keywords are added to the campaigns.
- Master / bad quality negative lists should be updated on a weekly basis.
Ad Group Structure
Your ad groups should be tightly-themed categories. This allows you to look at the ad group naming convention and immediately understand which keywords are in that ad group without having to see the actual keywords.

Once the ad groups are tightly themed (usually 3-6 keywords per ad group), you can create Ads that are directly based on the exact keywords that people are using to search for your company. For Broad, you can get more creative with your headlines because Broad keywords match with a wider range of queries. Aim for the highest possible CTR!

Youtube / Display Campaign Structure & Settings
An effective YouTube strategy requires a multi-layered approach; taking into account the various options for engaging with your target audience. A popular way to break out your campaigns is by separating them by the types of audiences you are targeting.
For example, in order to increase specificity, you might build out campaigns structured around the following types of audiences:
- Affinity
- In-Market
- Custom Intent
- Remarketing
Though all of these audiences can be a valuable component of your video or display campaign strategy, you will most likely find some of them to be far more effective than others in driving action throughout your lead funnel. Building out your campaigns in this way allows you to allocate budget accordingly and focus your spend on the most successful audiences.
Certain conditions, however, might warrant breaking out and structuring campaigns with more granularity. These conditions include geographical targeting, language, or categories of programs.
If you offer many types of programs, you can break out your targeting by program. This can keep your budgets aligned with specific program goals and prevent a more popular program from going through the entire budget. You will also be able to use different program-specific ad creative based on the audience type.
Ad Groups
Inside your YouTube campaigns, each one of your ad groups should be centered around a specific audience that coincides with the broader theme of the campaign. For example, your Custom Intent campaign might include ad groups focused on various types of custom intent audiences built around different keyword lists. Additionally, ad groups can be broken out even further based on factors like age, gender and other demographic details.
Structuring your ad groups in this manner creates the opportunity to show the most relevant ad creative for the given audience. This greatly increases the likelihood of further engagement with your content.
Other Key Video Campaign Settings
Much like any campaign on Google, success can easily be derailed if your campaign settings are incorrect.
A few quick notes about some settings you’ll want to pay special attention to:
Location Targeting
Careful consideration should be given to the locations you want your ads to target. Depending on your video advertising budget, you may wish to limit campaign geographical targeting to a more confined area than your search efforts. We always recommend excluding regions where you don’t want to pay for traffic.
If you have a physical campus, you can limit some campaigns to local prospective students who are more likely to enroll and allow those campaigns to run at higher CPA targets.
Networks
By default, most video ads are eligible to be shown on video partner sites in Google’s Display Network. While you may or may not want to exclude these placements from consideration for your video ads, we do recommend keeping a close eye on the traffic they bring in. We often find that this traffic is of poorer quality than general YouTube traffic. Thus, many of our clients have simply opted to turn it off.
Bidding Strategy
If you are running a campaign that is focused on driving conversions, you may find that there are limited options for bidding strategies. In most conversion-focused campaigns, you will have the option to run either a “Maximize Conversions” strategy, or a “Target CPA” strategy. Both of these approaches require accurate conversion tracking. You must also select the conversions you wish to optimize towards in the campaign “Conversions” setting.
The “Maximize Conversions” strategy allows Google Ads to set bids automatically to help you get the most conversions within your budget. Starting with this strategy gives the Google algorithm more flexibility to test your traffic and determine which ad placements and audiences are most likely to convert.
Once you have some data under your belt, you can consider switching to Target CPA, which will give the Google algorithm a specific cost-per-conversion to aim for.
If you import leads as well as applications into Google, you can run a lead generation campaign with the goal of generating leads for a low cost, and a performance campaign with the goal of maximizing applications.
The lead gen campaign will likely end up driving more traffic, which will be very useful for remarketing. However, traffic from the performance campaign will likely be of higher quality.
Content Exclusions
As important as it is to identify ad placements you wish to serve, it can be equally (if not more) important to identify placements you DON’T want to serve. Google gives you several exclusion options you can utilize to reduce poor quality traffic.
Those options are:
1. Inventory Type limitations: You can choose between Expanded, Standard and Limited inventories, which range from least to most restrictive based on profanity, sexual content and violence within content.

2. Excluded Content: You can specifically opt out of content that fits into certain categories. These categories are: tragedy and conflict, sensitive social issues, sexually suggestive content, sensational and shocking, and profanity & rough language. This exclusion setting gives you more control than the Inventory Type setting.
3. Excluded Types and Labels: Prevents your ad from showing on video content that belongs to any of the categories below:

4. Placement exclusions: You can get really granular and exclude specific websites, channels, videos, apps or app categories from showing your ads.
5. Excluded Topics: You may also select from a wide range of YouTube video topic categories on which you don’t want your ads to display.

Automation Best Practices & Integration (For SEM)
Many marketers use third party bidding tools to add a level of automation to their campaigns. These tools are able to measure additional data signals and therefore optimize accounts in ways that human beings could never do on their own. Another major benefit of automated tools is that they can almost optimize in “real time.” However, no tool can achieve true auction time adjustment.
Over the past 2-3 years, Google has significantly improved their own automated bidding solutions, which are available for no additional fee within the Google Ads platform. Google automation is the only way to perform auction time bidding optimizations, which can be extremely advantageous. With millions of data signals going into every auction, the bidding is optimized for each prospective student in accordance with the account’s goals.
Automation used to be a way to alleviate the pressure of manual bidding, while occasionally introducing another layer of data. Now, automation is driving massive improvements in performance and leaving manual-based strategies in the dust.

Best practices
Before implementing smart bidding, here are a few important tips we recommend:
Audit conversion actions – It’s crucial to fix any conversion tracking issues to ensure that conversion data is being reported properly. Then, you have to confirm that the right conversion actions are included in the Conversions column in Google Ads. In your account, go to Measurement > Conversions. Check the Include in “Conversions” column and see if the right conversions have the value as “Yes.”
Add first party audience lists to campaigns (Customer Match, RLSA, Similar Audiences) – These are lists of prospective students identified by first party data. They will provide Smart Bidding with more data so it can make better decisions on when to bid up or down on auctions.
Implement a non-last-click attribution model – Non-last-click models help you understand the exact value of each interaction with your Google Ads. Smart Bidding automatically assesses these touchpoints and prioritizes those that are most impactful. We recommend using a Data-Driven attribution model, if you meet the requirements for eligibility.
Give the AI some room – When implementing TCPA or other automated bidding strategies, it is tempting to tell the algorithm to hit some really low CPA and expect immediate results. But if you were getting a $150 CPA on manual, it is best to set a similar goal when implementing automated bidding and then gradually work it down. It might also take a few days for the algorithm to adjust to significant optimizations.
Different Smart Bidding Options (ROI Focused)
Target CPA – This drives as many conversions as possible, while maintaining your target cost per lead. If you have application or enrollment data imported into AdWords, you can set up TCPA to focus on more performance-driven conversion actions, as opposed to just leads.
Target ROAS – This drives the highest possible conversion value while maintaining your ROAS. This is only recommended if you’re able to import revenue-based data into your AdWords account.
When To Implement Google Ads AI
As I’m writing this in March 2020, I would suggest launching campaigns on manual CPCs for the first 30 days before shifting gears into eCPC for an additional 30 days.
Afterwards, I would start integrating TCPA on your lead generation campaigns after a substantial amount of data has been accumulated.

You want to get your campaigns to a point where there is enough data to create low or very low CPA fluctuation along with a fast or very fast initial learning period. At that point, you should be very confident that the campaign has enough data to switch from manual to AI.
Different Google Ads AI Options
Portfolio Smart Bidding – This is a goal-driven strategy that groups together multiple campaigns, ad groups and keywords. It can be very effective if you have multiple campaigns for the same programs that share the same goals. For example, if we were promoting a class for cyber security and you have several campaigns broken out by match types, we would want to group all the campaigns together into one portfolio bidding strategy. This way, the strategy aims to hit one goal across all of the campaigns.
Another major benefit of portfolio bidding is that the campaigns learn from each other in real time, which improves performance. This strategy is extremely effective for scaling enrollments while decreasing your cost per lead / cost per enrollments.

The data above showcases the performance of one of our EDU clients in the trade school vertical. We shifted to a fully-automated account by using portfolio bidding on all non-branded campaigns, which were broken out by programs.
This allowed us to generate over 12,000 more leads in 2019 for almost the same amount of money as 2018 because our portfolio bidding strategy helped us decrease our CPL from $114 to $94 after 2 years (2017 and 2018) of flat CPL performance.
Campaign Smart Bidding – This is the process of creating a TCPA goal on a campaign-by-campaign basis. Campaign Smart Bidding is particularly useful when you’ve consolidated devices and match types into one campaign for the same program or goal.
Ad Group Smart Bidding – Once you’ve activated campaign TCPA, you can start changing TCPA goals by ad groups. I would not recommend using this strategy. If you’re using Ad Group Smart Bidding, it’s probably because your campaign structure is not organized properly.
Final Tips
The more data you consolidate for Google to analyze, the more success you will have with automation. That’s why I am a strong believer in portfolio bidding. You can have granular campaigns / ad group structure, but still consolidate all the respective campaigns into portfolio bidding strategies so they can learn from each other and make decisions that are simply not possible with manual. If you’re not using automation today, you’re leaving a significant amount of opportunity on the table. Manual bidding doesn’t come close to what the automation can do.
When Not To Use Automation
Stability issues & bugs – Google regularly updates this part of their software. When bugs are discovered, the advertisers eat up the cost. It’s safe to assume there will always be bugs but don’t expect Google to disclose this because there is no way for us to prove it (or sometimes even notice it).
Control – Allowing AI to handle most of our tasks as marketers sacrifices a great deal of control over the account. For example, if we want to increase or decrease spend, we’re not able to do this as quickly under an AI bidding strategy compared to manual bidding.
Branded campaigns – AI can overpay for branded keywords if we’re not careful. Since most Branded keywords have a quality score of 10/10 and there shouldn’t be much reason to regularly change bids for these keywords, we should stick to manual.
Optimizing Based On Applications, Enrollments & Revenue (Quality VS Quantity)

We have the ability to optimize based on audiences, strategies or keywords that are driving applications and enrollments, as opposed to just leads. Optimizing on strategies that are driving action will help improve lead quality, decrease costs and scale enrollments.
If you are currently optimizing your campaigns based on lead data, your performance might look like this:

With Google Ads, we are able to measure offline conversion events up to 90 days after the click by importing offline events directly into Google Ads. This gives us a deeper and more granular understanding of how each click drives offline actions.
After successfully importing back-end data into Google Ads, we can easily distinguish clicks and queries that produce low quality leads from those that produce high quality leads. Leveraging these new sets of data points allows us to unlock better bid optimizations.
How It Works

Before you start the implementation process, it’s important that you do the following steps:
- Enable Auto-Tagging in Google Ads: Auto-tagging will attach the “Google Click ID” (GCLID) parameters to the URL the user clicks.
- This GCLID (<=120 characters long) lets Google know which click to attribute the conversion event back to
- Make sure the key stakeholders in your education organization are aligned
- Make sure your lead management tool/CRM can store GCLID
- Change your click to conversion cycle to be less than 90 days
The Path To a Successful Implementation

Successful and smooth implementation is not possible without the right team members:

The following section goes into great detail on how to integrate back-end data
Step 1 – Create a new conversion action in Google Ads (Google Ads Manager)

- Create in the Google Ads account or at a Manager (MCC) account level
- When creating new conversion, select “Import”
- Attribution window: 90 days
- Initially, do not include in conversions column
Step 2 – Modify lead form by adding a hidden field in your website’s lead form that will pass the GCLID through the CRM (CRM administrator + Web developer)

- In order to pass the GCLID to your database/CRM, you will need to add a hidden form field to each lead form on your site.
- The Javascript you implement in Step 4 will then insert the GCLID into this new field.
- In most cases, you will need to collaborate with your database/ CRM admin on this step
Step 3 – Modify CRM back-end to ensure that the CRM will store the GCLID (CRM administrator)

- Modify the CRM so that the GCLID passed from the lead form can be captured and stored alongside other lead details (typically in the lead and opportunity objects).
- Later, you will query these objects to determine which have converted and which GCLID and related info to pass back to Google.
Step 4 – Implement Javascript to capture the GCLID when the user arrives on the site and store the value so it can be retrieved later. (Web developer)

- Insert the value into the new form field
- Update the script so it can identify the ID of the hidden GCLID field in your website’s form that was added in step 2
- Then insert this code on every page on your website
Quick Recap: What has happened so far


Step 5 – Extract & format the conversion data

Step 6 – There are a few ways to import this data into Google. The first two are more on the manual side and the last two are more on the automated side.
The following steps involve four options for importing back-end data, with each option offering a different level of manual and automation.

Option 1
Manual upload – upload CSV, Excel, or Google Sheets files directly into the Google Ads via the user interface.
Option 2
Schedule Upload – Schedule a regular upload from Google Sheets, a web server, or an SFTP server. Choose the frequency with which you’d like us to upload your conversions
Option 3
API Upload – Upload conversion data via the Google Ads API
Option 4
CRM Integration – Import conversions automatically from salesforce sales cloud or using Zapier.
Below are instructions on how to import the data directly into Google Ads. The following information covers options 1 and 2. For options 3 and 4, we recommend jumping on a call with your CRM developer, web developer, your Google rep and your Google Ads account manager to integrate via API / CRM.
Prepare the data for upload
Required fields are:
- Google Click ID (GCLID)
- Conversion Name Created in Step #1
- Conversion time – when the student was enrolled. NOT when click came in.

Optional Fields
Conversion Value or Revenue (required for TROAS smart bidding)
Conversion time refers to when the conversion happened (e.g when the student has enrolled), not the time of click. Date/time formatting can be a source of errors when importing, so please look out for that.

Step 7 – Setting up the upload into Google Ads in a few easy steps

When uploading from Google sheets, remember to share access with the specified mail address and always preview for errors before you upload

Step 8 – Preview before upload!!

You can still troubleshoot errors after preview and then re-upload your file.
Once you have finished with the preview you can choose to APPLY FILE.
Duplicate entries are avoided as Google Ads won’t re-upload a conversion that has the same combination of GCLID, Date/Time and Conversion Name.
ACTION: This is one of the most important integrations for education companies. It will allow you to STOP guessing and START distinguishing what works from what’s driving useless leads. Ultimately, you will increase your enrollments while decreasing your cost per enrollments.
Depending on the number of actual enrollments, it might be better to optimize based on applications or whatever your third step of the funnel is (some sort of qualification after the lead).
If you can’t figure out how to manually upload or get your CRM connected to Google, talk to your Google team about connecting your CRM with Google Ads through Zapier. Zapier is a workflow automation tool that helps you connect Google Ads to 1,500+ other apps.
The Future of Google Ads & How To Prepare For It
Over the past 7 years, I’ve watched Google Ads (previously known as AdWords) gradually decrease the amount of control it provides over how your money is being spent.
The future of Google Ads is focused on audiences and automation. I believe Google will soon remove the ability to bid on keywords for PPC and completely transition to audiences (like YouTube & Display).
That might come as a huge shock to some people. But over the past few years, Google has already moved in this direction by removing more and more control from Exact, Phrase and BMM match types.
Google’s first major step towards my prediction will be removing exact, with Phrase/BMM following shortly after. The only remaining option – Broad – will last another two years at most.
After that, Google will fully transition to an audience and automation-based approach across all channels, as their technology continues to improve.
The best way to prepare for these shifts in SEM is to start building your strategies with an audience mindset and transition from manual to automation bidding. The more test & learn you accomplish today, the more success you will find in the future.

